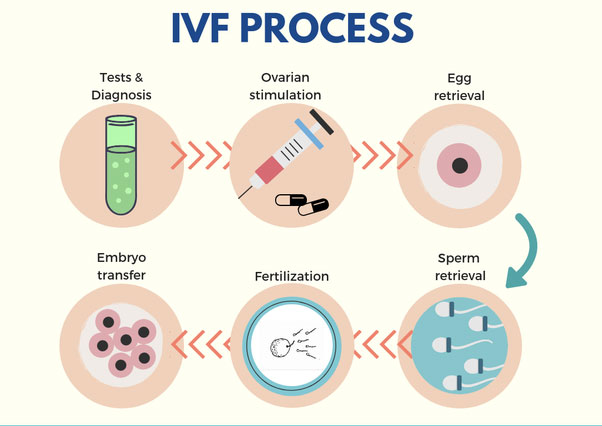
IVF diet to boost success rate of IVF treatment
March 31, 2020
5 Ways to boost your fertility with nutrition
April 12, 2020In our modern day-to-day life, we come into contact with several different chemicals through the products we use, the food we eat, and the air we breathe. Studies indicate that a specific group of chemicals called endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) may have adverse effects on female and male reproductive health.

If you’re planning a normal or IVF pregnancy, or if you’re already pregnant, here’s what you need to know about EDCs and how to avoid to increase your chances of successful IVF pregnancy.
What are endocrine-disrupting chemicals?
EDCs are substances that can be found in the air, soil, water, food, and manufactured products. They can interfere with the body’s normal functioning, including the reproductive systems of women and men. Some EDCs occur naturally in food. Soybeans and flax seeds, for example, are high in a substance called phytoestrogen which mimics the effects of the female sex hormone estrogen. However, you would need to consume an awful lot of these foods for the phytoestrogen to affect you.
But the point of concern is that there are about 800 artificial EDCs in everyday items, so to have a high success rate of your IVF treatment you should minimize their exposure on your body, these items are including such as food container plastics, personal care items, and food products. EDCs are also present in manufacturing and agricultural operations. Regardless of their many different sources, we are all exposed to EDCs, but the exposure varies depending on your work, lifestyle choices, and location.
What EDCs may affect the success of IVF treatment?
Because we are exposed to combinations of so many various types of chemicals, it is often hard to know precisely how particular chemicals affect our health. But in the case of EDCs, research has found that male and female reproductive health may be adversely affected by mimicking or blocking male and female sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone). It can cause: changes in levels of hormones, decreased sperm and egg quality, sperm DNA damage, longer menstrual cycles, taking longer to achieve a pregnancy, increased risk of miscarriage, and early menopause.
Evidence indicates that EDCs are found in 95% of people studied, and some EDCs are higher in people who are infertile. People who are exposed to high levels of certain EDCs through their profession have increased fertility risk. Particularly, higher rates of certain EDCs decrease the chance of getting pregnant among couples using assisted reproductive technology (ART).
How to reduce exposure to EDCs
While we can not avoid exposure to EDCs, we can start taking some basic steps to reduce exposure to EDCs. This is particularly important for women and men who are planning or undergoing IVF treatment. You can talk to us or contact us about what precautionary measures you can take to reduce the risks of EDCs when planning IVF treatment.
10 useful tips for reducing exposure to EDCs:
- Wash fruit and vegetables reduce the intake of pesticides, fungicides, herbicides, and chemicals that may have been sprayed on plants.
- Eat less processed, canned, pre-packaged foods reduces your intake of BPAs, phthalates, and plasticizers that coat the inside of cans or are absorbed from plastic wraps or cling wrap or foil.
- Limit your mobile usage as it may expose your hands to the plastic while using it.
- Limit your intake of oily fish (salmon, tuna, sardines) and fatty meat reduces your intake of POPs, pesticides, heavy metals and fat-soluble chemicals that may accumulate in animals.
- Avoid handling or storing sales receipts in your wallet. The thermal coating contains BPA to give them a glossy plastic texture.
- Drinking water / soft drinks from glass or hard plastic bottles, not soft plastic bottles and disposable plasticware. BPA, phthalates and other plasticizers are used to make plastics flexible in bottles.
- Never heat food in soft plastic takeaway containers as well as those covered with cling wrap or foil. Alternatively, place the food in a china or glass bowl and cover with a paper towel or china plate before heating. When heated, phthalates and bisphenols in plastic can quickly be absorbed into the food, particularly when they are fatty. The process of heating also releases dioxins from plastics which can be absorbed into the food.
- Avoid air fresheners, smoke, strong chemicals, highly perfumed products, plastic smells and fumes that air your home often reduce the amount of inhalable chemical particles avoid the use of pesticides and herbicides in the garden, at work or at home. Instead, try using ‘green chemicals’ that use non-toxic agents to reduce pests and weeds.
- Minimize the use of potent household products such as heavy detergents, hand sanitizers, cleaning agents and carpet cleaners or strong chemicals such as glues, paints, and varnishes that have a wide range of chemical classes in them. Use ‘green products’ that use alternative non-toxic agents.
- Read labels on all personal care products such as cosmetics, shampoos, conditioners, hair coloring, and body washes, etc. and choose those that are free of parabens. Try to avoid the use of highly perfumed/scented products where possible.
- Read labels on all food products and avoiding those with additives, preservatives and anti-bacterial agents that are aware of marketing ploys-some products that are advertised as ‘BPA free,’ for example, often use similarly harmful to substitutes such as BPS.